We looked under the hood of the popular browsers Firefox and Chrome and now it’s time to find out which one comes out first in a duel.
Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox are among the most popular web browsers used on the PC and are thus also the most widespread ones. Both apps also have phone and mobile (tablet) versions making it easy to keep your data and bookmarks synched across multiple devices. This way you can synchronize settings, favorites, etc. among your devices without using additional software.

Since Microsoft have said goodbye to Internet Explorer and, in Windows 10, released a new browser called Microsoft Edge, more users are looking for an alternative. The popular choice are Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
We’ve looked at both bowsers. According to Statista market research, Google Chrome holds the biggest part of the market share at 58%, followed by Firefox at 13%. Microsoft’s Internet Explorer only rakes in 8% – Edge currently occupies 3%. While there are different sources for market share, however Chrome and Firefox always top the list when it comes to browsers.
Firefox vs. Chrome
Google Chrome – A Data Leech?
There are still plenty of rumors that say that Google’s privacy protection in Chrome is worse than in other browsers. In current versions however, this is not the case anymore. A lot less data is being tracked by Chrome than has been in previous versions – no more than any other browsers do. Google Chrome surely is among one of the fastest, if not the fastest, browsers on the market right now. Updates for Chrome and Firefox are being released on a regular basis meaning safety loopholes are being closed quickly.
Most functions of both browsers are pretty much identical. Nowadays, it’s the standard for browsers to have an intelligent address bar allowing you to enter URLs as well as using it as a search field. Both browsers support Google search among other options for search engines. Different themes are also available for both browsers and make it possible to design them to your liking. Both browsers also support add-ons. This can be accessed in the “Options” section.
Google Chrome: Many Versions and Functions
Google Chrome is available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux in 32 and 64-bit versions, as well as for smartphones and tablets running Android or iOS. The browser by itself comes with numerous features like viewing PDFs directly in the browser without the need for plugins. Using the integrated Chrome Web Store, third-party developers are offering plenty of add-ons and plugins for the browser.
Same is true also for Mozilla Firefox. Generally speaking, most add-ons available for Firefox are also available for Google Chrome and vice versa. If not, there will be alternatives. Chrome allows you to log in with your Google account making it possible to sync settings and bookmarks across all your devices you installed Chrome on. While this is also possible with Firefox, a Google account does offer a lot more functions.
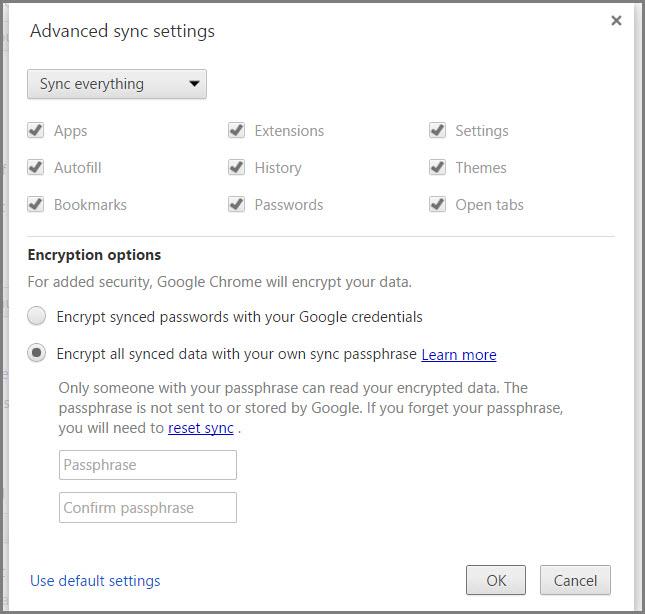
After logging in with your Google account, you’ll be able to use a plethora of syncing options in Chrome.
High Performance and Stability in Google Chrome
It’s great performance stems from Chrome’s ability to manage individual processes within the browser. The individual tabs are realized as individual tasks which improves stability and performance. This also means that one hardware intensive tab won’t slow down the others. If one website happens to crash, the other tabs remain usable. Individual tabs can be closed using Google Chrome’s integrated task manager. This can be accessed by pressing Shift+Esc or through the dropdown menu.
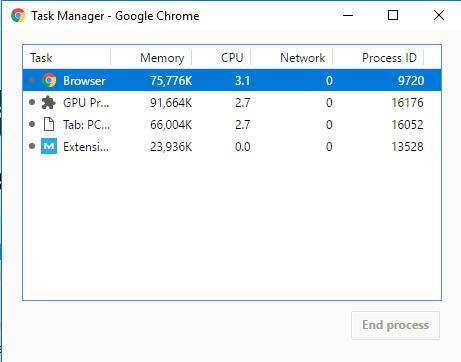
Google Chrome has its own task manager allowing you to quit individual tabs.
Safety in Google Chrome
By nature, Google Chrome is very safe and nowadays usually tops the charts when it comes to testing browser safety. Those who need even more safety can install additional add-ons that improve various aspects. Since the newest Chrome updates can be installed automatically during use, even less tech-savvy users are able to always use the latest version of Chrome. Chrome not only has plenty of features, but is also great in the safety department. Chrome, much like Firefox, features a spam-blocker and an incognito (or private) mode.
All of these functions can be further expanded using add-ons. Google Chrome allows you to deactivate JavaScript which is only possible in Firefox using an add-on (while offering some more features however). To accomplish this in Firefox, add-ons like Ghostery or NoScript are great. Flash and other forms of interactive web content can also be limited by Chrome. With Firefox, plugins are required for this. Chrome’s Flash Player is separated from your system which protects your machine from harmful Flash code. The player is regularly being updated alongside Google Chrome.
Firefox and Chrome both offer password management with the one in Chrome not being as secure as that in Firefox however. Here, Mozilla has trumped Google by making it possible to protect all your passwords using one master password. Both browsers feature rudimentary protection against malware and phishing websites.
Google Chrome offers a clean and simple user interface as well as sufficient security features.
Mozilla Firefox – Internet Explorer’s Arch Rival
Mozilla Firefox originally became popular as Microsoft Internet Explorer’s arch rival. Now, developers at Google are competing by adding numerous features and functions to Chrome.
There are plenty of add-ons for Firefox that can significantly increase its functionality. Due to its long history, it can still easily compete with Chrome. It also offers more customization options and can still compete with independent browsers such as Tor in the safety department.

Mozilla Firefox is getting more and more modern and only lacks a few features that Google Chrome comes with.
In addition to this, Firefox offers a download accelerator, video accelerator, and a hardware accelerator. While these features are missing in Chrome, it certainly isn’t slower than Firefox. In terms of CPU usage, both browsers behave similarly.
Mozilla Firefox: Simple to Use as Well
Firefox allows you to create custom shortcuts, a feature that Chrome doesn’t offer on its own. As with Google accounts in Chrome, Mozilla Firefox also allows you to sync bookmarks, passwords, settings, and browsing history using an account. One of Chrome’s advantages here is that users can directly access Google services like Google Mail or YouTube.
Since Mozilla Firefox is independent of other software applications, many browser settings are easier to adjust than they are in Google Chrome. Google of course has the interest of persuading Chrome users into using Google products. Firefox for example makes changing your default search engine much easier. While Google is the default setting, Yahoo, Bing, the safe search engine DuckDuckGo, and the translation service Leo are integrated from the get-go. The settings can easily be adjusted within the search bar itself. Additional search engines can also be integrated. Of course, both browsers allow local text search om the current page by pressing Ctrl+F. Any matches will be highlighted on the page. Like Google Chrome, Firefox also has an integrated PDF viewer.
Safety in Mozilla Firefox
Like in Google Chrome, Firefox also has more than decent security features. The developers are releasing new updates on a regular basis closing security breaches in the process. Many users prefer using Firefox because they don’t trust companies like Google or Microsoft. Firefox thus is still a suitable underdog solution. One advantage it has in the safety department is the possibility of protecting all your passwords using a master-password. This is a feature not available in Chrome. However, this function needs to be activated manually in the settings.
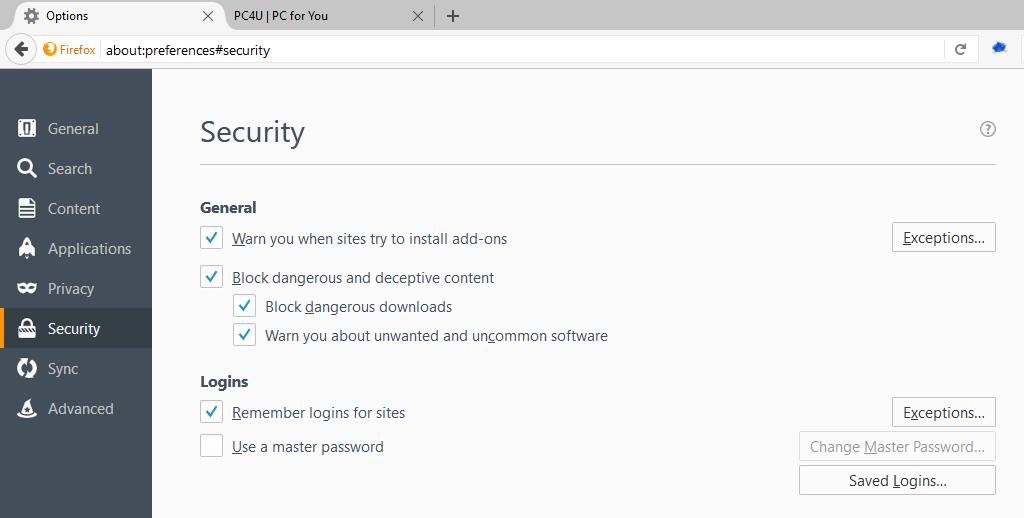
Mozilla Firefox protects all saved passwords with a master password.
Firefox has the advantage of a big third-party developer community and plenty of add-ons as a result. Most notably, there are lots of safety add-ons, that makes the browsers safety features even more adjustable than in Google Chrome. While you’ll have to manually install add-ons to reach Google Chrome’s level of safety, the Firefox add-ons give you more options to configure your safety options.
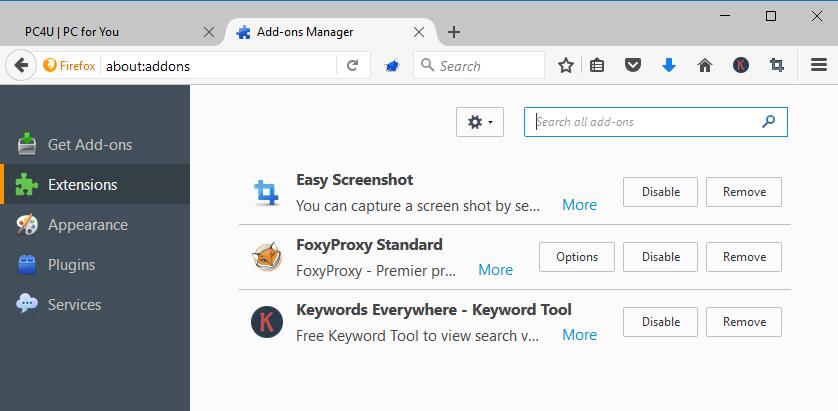
Mozilla Firefox can be expanded more drastically using add-ons than Google Chrome.
Conclusion
Google Chrome shows its advantages mainly in its high speed and ease of use. Mozilla Firefox on the other hand is more customizable in a lot of ways. Safety-wise, they’re relatively equal. The password protection in Mozilla Firefox however, is somewhat more trustworthy. Both browsers have a mobile version making them available on non-PC devices as well.