It is known that a proxy is connected to a remote computer and a VPN network is also connected to a remote computer, so one would imagine they’d be the same, but it is not so, because proxies are a poor substitute of VPNs.
Every two weeks there is an important story about encryption, data filtering, IGMP, or other digital privacy issues. Many of these articles speak of the importance of security your Internet connection can have, such as using a VPN (virtual private network) when you are in a public place on a Wi-Fi network.
Even though they are completely different, virtual private networks and proxy servers have only one thing in common: both allow you to appear as if you’re connecting to the network from another location. They also offer privacy, encryption, and other functions, however, it varies greatly from one to another.
Proxies hide your IP address
A proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary in the flow of Internet traffic, so your activities on the Internet seem to come from elsewhere. Traffic from the web browser could come from the remote computer and not your own.
For example: Several people in their homes play an online game where a daily bonus for voting for the game on a website server is obtained. However, the website has a policy of one vote per IP, regardless of whether different player names are used. Thanks to proxy servers every person can register their vote and get the bonus in the game because it gives the feeling that the web browser from each person seems to come from a different IP address.
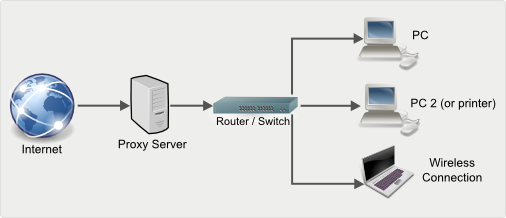
The main purpose of a proxy server is to hide your IP address and act as an intermediary in your Web browsing. By this I mean that what it does is swap your IP with another and makes it look like you’re browsing from another computer, but encryption and privacy are not insured.
What happens in a proxy server it is that security is not guaranteed and any user has the ability to spy and we are vulnerable to any kind of cybernetic attack.
The VPN encrypt your connection
Networks such as proxy servers, make your browsing seem as if it were a remote IP address. This means that unlike a proxy server, which simply acts as an intermediary for a single program (such as the web browser or a BitTorrent client), virtual private networks (VPN) capture traffic from every request on your computer from your web browser, either for your online games or even for updates that Windows is running in the background.
This whole process passes through an encrypted tunnel between the computer and the remote network. This makes a VPN connection the ideal solution for any high range network where the use of privacy and anonymity is the main objective. With a VPN, neither your Internet provider nor any other party can access the transmission between your computer and the server.
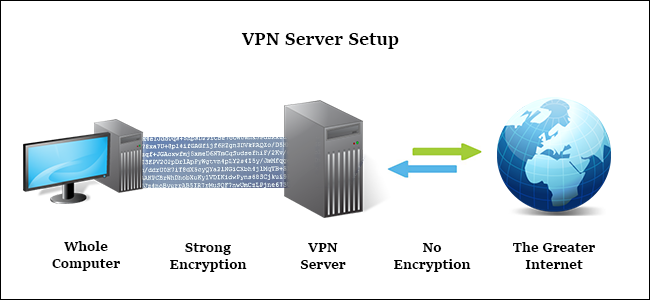
With a VPN enabled, you don’t have to worry about Wi-Fi safety practices in cafes networks or free Internet access in your hotel being vulnerable.
Although VPNs are secure, they’re not without their drawbacks. Running a VPN requires good hardware and as such, VPN services are not free (although some providers, such as TunnelBear, offer us a free package). Usually you must pay at least a few dollars a month for a VPN service.
It is very clear that VPNs require high performance on your computer, however, proxy servers don’t have additional costs when used. VPNs need bandwidth and processing.
In summary, proxy servers are efficient to hide your identity during usual activities done in your browser, but when it comes to specific activities that require protection against espionage, you need a VPN.